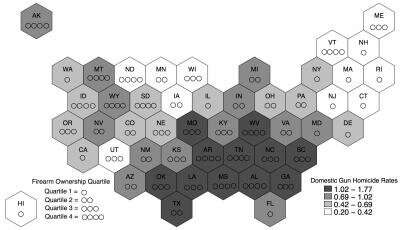
 A new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, reveals a unique and strong association between firearm ownership and the risk of domestic homicides. For each 10 percent increase in household gun ownership rates, the findings show a significant 13 percent increased incidence of domestic firearm...
A new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, reveals a unique and strong association between firearm ownership and the risk of domestic homicides. For each 10 percent increase in household gun ownership rates, the findings show a significant 13 percent increased incidence of domestic firearm...
GASTROINTESTINAL
You can add some category description here.
 A new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, reveals a unique and strong association between firearm ownership and the risk of domestic homicides. For each 10 percent increase in household gun ownership rates, the findings show a significant 13 percent increased incidence of domestic firearm...
A new study in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, published by Elsevier, reveals a unique and strong association between firearm ownership and the risk of domestic homicides. For each 10 percent increase in household gun ownership rates, the findings show a significant 13 percent increased incidence of domestic firearm...
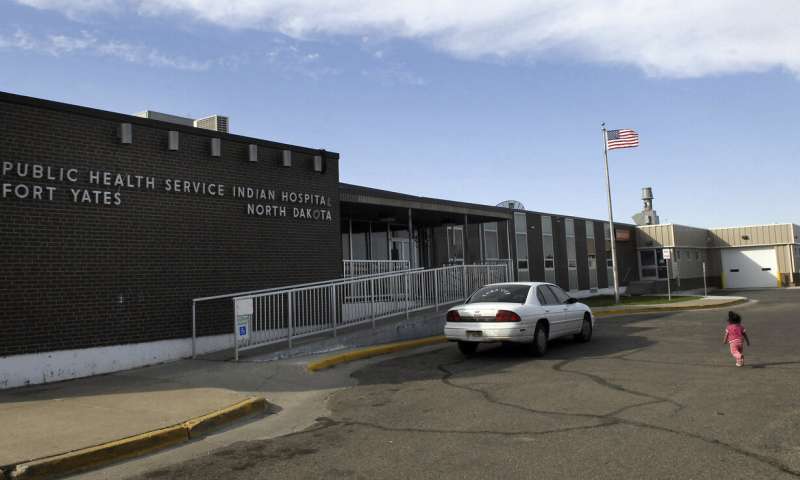 Government hospitals placed Native American patients at increased risk for opioid abuse and overdoses, failing to follow their own protocols for prescribing and dispensing the drugs, according to a federal audit released Monday. The report by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General doesn’t draw...
Government hospitals placed Native American patients at increased risk for opioid abuse and overdoses, failing to follow their own protocols for prescribing and dispensing the drugs, according to a federal audit released Monday. The report by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General doesn’t draw...
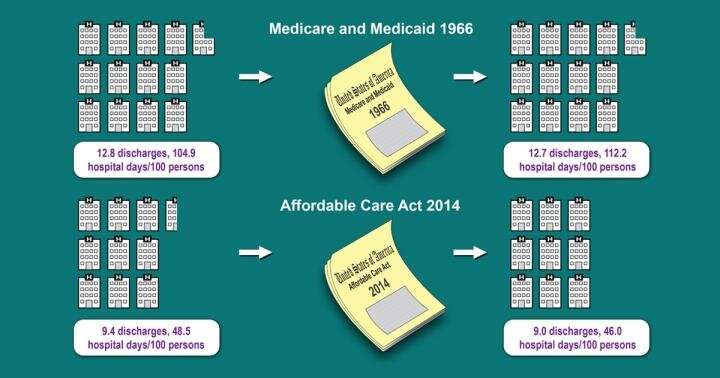 As political leaders debate the merits of a future Medicare for All system in the U.S., some analysts predict that implementing universal coverage could cause a sharp, unaffordable increase in hospital use and costs, overwhelming the system. But new research by a team at Harvard Medical School and The City...
As political leaders debate the merits of a future Medicare for All system in the U.S., some analysts predict that implementing universal coverage could cause a sharp, unaffordable increase in hospital use and costs, overwhelming the system. But new research by a team at Harvard Medical School and The City...
 (HealthDay)—It seems as though every day brings yet another study on the effects of caffeine or coffee in particular. Researchers have looked at its effects on almost every aspect of health, from overall mortality to the heart, bones, kidneys, liver, fertility and more. Sometimes, separate studies on the same aspect...
(HealthDay)—It seems as though every day brings yet another study on the effects of caffeine or coffee in particular. Researchers have looked at its effects on almost every aspect of health, from overall mortality to the heart, bones, kidneys, liver, fertility and more. Sometimes, separate studies on the same aspect...
 A new study has found that an Inuit population in Canada’s Arctic are genetically distinct from any known group, and certain genetic variants are correlated with brain aneurysm. Geographically isolated populations often develop unique genetic traits that result from their successful adaptation to specific environments. Unfortunately, these adaptations sometimes predispose...
A new study has found that an Inuit population in Canada’s Arctic are genetically distinct from any known group, and certain genetic variants are correlated with brain aneurysm. Geographically isolated populations often develop unique genetic traits that result from their successful adaptation to specific environments. Unfortunately, these adaptations sometimes predispose...
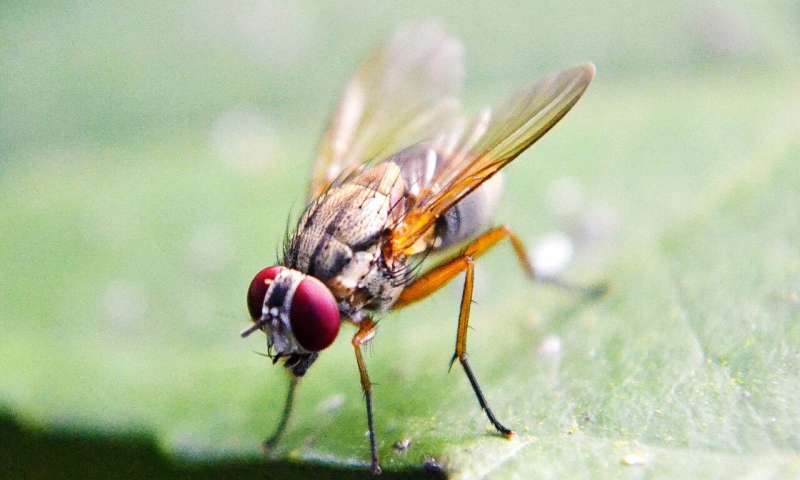 When a fruit fly decides it wants to walk in a particular direction, it sticks to its plan with impressive resolve. Now, Rockefeller scientists have begun to understand how insect brains make and meet navigational goals. In monitoring itinerant flies, the researchers showed that the animals compare their current heading...
When a fruit fly decides it wants to walk in a particular direction, it sticks to its plan with impressive resolve. Now, Rockefeller scientists have begun to understand how insect brains make and meet navigational goals. In monitoring itinerant flies, the researchers showed that the animals compare their current heading...
 How well you manage your money in college may determine when you’ll ultimately achieve “adult identity,” according to a new study led by the University of Arizona. Researchers tracked a group of students from their fourth year of college to five years post-graduation. Participants were asked at three different points...
How well you manage your money in college may determine when you’ll ultimately achieve “adult identity,” according to a new study led by the University of Arizona. Researchers tracked a group of students from their fourth year of college to five years post-graduation. Participants were asked at three different points...
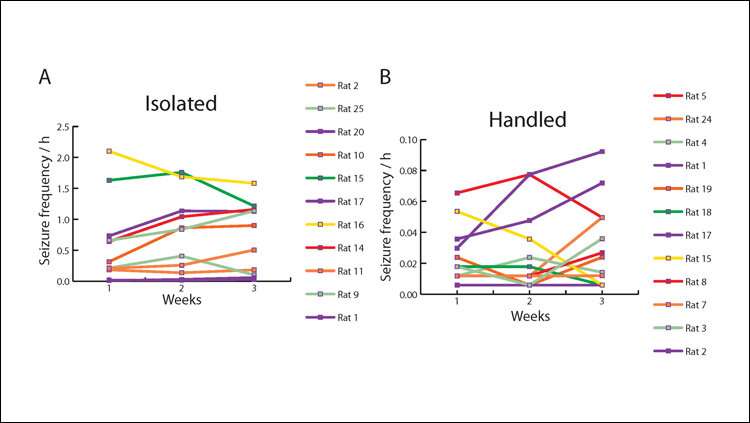 The traditional method of housing mice and rats alone increases stress and worsens epilepsy, according to a new study published in eNeuro. The added stress could complicate results of pre-clinical drug trials. Rodents are typically housed alone to prevent aggressive behaviors and simplify data collection. However, rats and mice are...
The traditional method of housing mice and rats alone increases stress and worsens epilepsy, according to a new study published in eNeuro. The added stress could complicate results of pre-clinical drug trials. Rodents are typically housed alone to prevent aggressive behaviors and simplify data collection. However, rats and mice are...
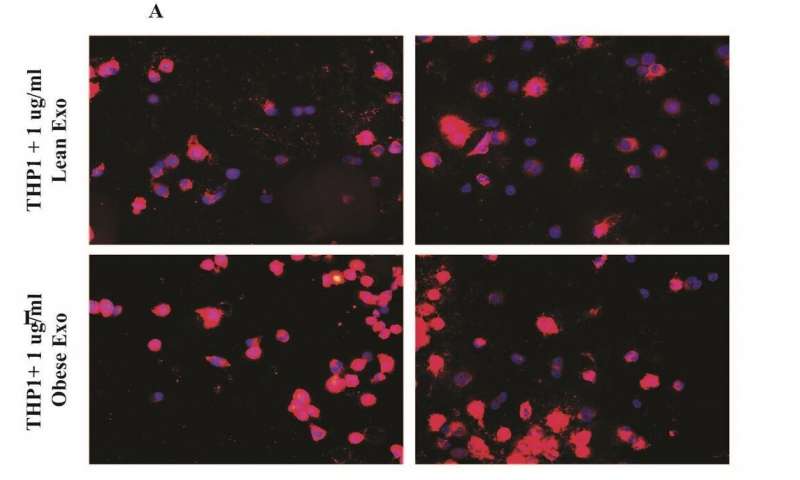 A multi-institutional team led by research faculty at Children’s National in Washington, D.C., finds that extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from kids’ fat can play a pivotal role in ratcheting up risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease well before any worrisome symptoms become visible. What’s more, the team showed that EVs found...
A multi-institutional team led by research faculty at Children’s National in Washington, D.C., finds that extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from kids’ fat can play a pivotal role in ratcheting up risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease well before any worrisome symptoms become visible. What’s more, the team showed that EVs found...
 A paper published in Scientific Reports describes how researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo’s Medical School (FM-USP) in Brazil and colleagues at institutions in Europe evaluated behaviors leading to weight gain in adolescents. Childhood obesity can favor the premature emergence of health issues such as type 2 diabetes...
A paper published in Scientific Reports describes how researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo’s Medical School (FM-USP) in Brazil and colleagues at institutions in Europe evaluated behaviors leading to weight gain in adolescents. Childhood obesity can favor the premature emergence of health issues such as type 2 diabetes...
